General Properties of Salts






General Properties of Salts
General Properties of Salts:
Salts are the white crystalline powder formed due to neutralization reaction of an acid and a base. Salts show following general properties:
1. Melting and boiling points:
Salts are mostly solid which melt as well as boil at high temperature.
2. Water of crystallization:
Salts are found as crystals with water molecules present in them. This water is called water of crystallization and such salts are called hydrated salts. E.g.: copper sulphate . On heating, hydrated salts lose their water of crystallization, crystals lose their shape, color and change to a powdery substance. The hydrated salt that have lost their water of crystallization are called anhydrous salts.
3. Hydrated and Anhydrous Salts:
The crystals of some salts have a fixed number of water molecules (called water of crystallization) loosely associated with them such salts are called hydrated salts. These hydrated salts on heating lose their water of crystallisation and change to powdery substance called anhydrous salt.
4. Reaction with an Acid:
When a salt reacts with an acid, another salt and acid are formed. For example, when sodium chloride is heated with sulphuric acid, sodium hydrogen sulphate (at low temperature) and then sodium sulphate (at high temperature) are produced and hydrogen chloride gas is evolved.
5. Reaction with a Base:
A salt reacts with a base to produce another salt and base.
6. Reaction with a Metal:
Sometimes, a salt solution may react with a metal. For example, when an iron nail is dipped into an aqueous solution of copper sulphate, copper gets deposited on the surface of the nail and the ferrous sulphate formed remains in the solution. This reaction shows that iron is more reactive than copper. Thus, a more reactive metal can displace a less reactive metal from a solution of its salt.
7. Behavior of Salts towards Water:
Salts are soluble in water. Eg: sodium chloride, potassium sulphate, lead chloride, copper carbonate etc are soluble in water.When a salt is dissolved in water, the solution may be neutral, acidic or alkaline. This depends upon the nature of the salt used.
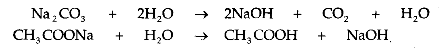

Salts are mostly solid which melt as well as boil at ____________________ . | |||
| Right Option : B | |||
| View Explanation | |||
When hydrated | |||
| Right Option : A | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Which of the following is a basic salt? | |||
| Right Option : C | |||
| View Explanation |
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
About Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.

Shreya Shrivastava
8thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thI have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying

Yatharthi Sharma
10thAbhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.

Om Umang
10thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thOne of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thIt has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.
